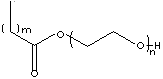| POLYETHYLENEGLYCOL MONOLAURATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO | 9004-81-3 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
| |
| MOL WT. | ||
|
H.S. CODE |
||
|
TOXICITY |
|
|
| FORMULA | C11H25COCO(CH2CH2O)n | |
| SYNONYMS | polyglycol Monolaurate; | |
| Oxyethylenated Lauryl alcohol; POE Monolaurate; POE Monolaurate ether; Polyoxyethylene Monolauryl ether; Poly(oxyethylene) Monolaurate; Polyethylene glycol Dodecyl ether; | ||
SMILES |
||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
SURFACTANT |
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
light amber semisolid | |
|
MELTING POINT |
||
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Dispersible | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
Polyethylene glycol is a condensation polymers of ethylene oxide and water with
the general formula H(OCH2CH2)nOH, where n is the average number of repeating
oxyethylene groups typically from 4 to about 180. The low molecular weight
members from n=2 to n=4 are diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol and
tetraethylene glycol respectively, which are produced as pure compounds. The low
molecular weight compounds upto 700 are colorless, odorless viscous liquids with
a freezing point from -10 C (diethylene gycol), while polymerized compounds with
higher molecular weight than 1,000 are waxlike solids with melting point upto 67
C for n 180. The abbreviation (PEG) is termed in combination with a numeric
suffix which indicates the average molecular weights. One common feature of PEG
appears to be the water-soluble. It is soluble also in many organic solvents
including aromatic hydrocarbons (not aliphatics). They are used to make
emulsifying agents and detergents, and as plasticizers, humectants, and
water-soluble textile lubricants.Polyethylene
glycol is non-toxic, odorless, neutral, lubricating, nonvolatile and
nonirritating and is used in a variety of pharmaceuticals and in medications as
a solven, dispensing agent, ointment and suppository bases, vehicle, and tablet
excipient. Lipophilic compounds are ethoxylated ethylene oxide (the monomer of polyglycols)
so that the target compounds have hydrophilic (soluble in water). The
bifunctionality in one molecule provides the basic properties of surfactants.
Fatty acids rather lipophilic (or hydrophobic) exhibiting low HLB
(Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance) values; having an affinity for, tending to
combine with, or capable of dissolving in lipids (or water-insoluble). While,
the ethoxylated fatty acids are hydrophilics exhibiting high HLB values; having
an affinity for water; readily absorbing or dissolving in water. The type of
fatty acid and the mole number of ethylene oxide provides diverse HLB values for
proper applications. There are almost
infinite ethoxylated compounds. In combination with the average molecular weights
and water-soluble property of PEG, the wide range of chain lengths of
fatty acids provide identical physical
and chemical properties for the proper application selections directly or
indirectly.
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Esters are non-toxic and non-irriting nonionic emulsifiers. They are prepared by the esterification of fatty acids with polyethylene glycols. The low molecular weight ranging PEG Esters are oil-soluble to work in nonaqueous systems. The high molecular esters are water-soluble can be used in aqueous systems. Polyethylene Glycol Esters are used as emulsifiers and in formulating emulsifer blends, thickener, resin plasticizer, emollient, opacifier, spreading agent, wetting and dispersing agent, and viscosity control agents. They also have application in the metalworking, pulp, paper, textile and as defoamers for latex paints. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
PEG 200 ML |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
light amber liquid | |
|
MELTING POINT |
4 - 5 C | |
|
ACID VALUE |
5 max | |
| SAP VALUE |
132 - 142 | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.983 ± 0.010 | |
| CLOUD POINT (1% H2O) |
15 C | |
|
APPRX HLB |
9.2 | |
|
PEG 300 ML |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
light amber liquid | |
|
MELTING POINT |
7 - 8 C | |
|
ACID VALUE |
5 max | |
| SAP VALUE |
104 - 114 | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.010 ± 0.010 | |
| CLOUD POINT (1% H2O) |
45 C | |
|
APPRX HLB |
11.4 | |
|
PEG 400 ML |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
light amber liquid | |
|
MELTING POINT |
11 - 13 C | |
|
ACID VALUE |
5 max | |
| SAP VALUE |
86 - 96 | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.024 ± 0.010 | |
| CLOUD POINT (1% H2O) |
66 C | |
|
APPRX HLB |
13.0 | |
|
PEG 1000 ML |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
light amber solid | |
|
MELTING POINT |
40 - 41 C | |
|
ACID VALUE |
5 max | |
| SAP VALUE |
40 - 50 | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.035 ± 0.010 | |
| CLOUD POINT (1% H2O) |
> 80 C | |
|
APPRX HLB |
16.5 | |
|
PEG 4000 ML |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
light amber solid | |
|
MELTING POINT |
55 C | |
|
ACID VALUE |
5 max | |
| SAP VALUE |
10 - 18 | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.075 ± 0.010 | |
| CLOUD POINT (1% H2O) |
> 100 C | |
|
APPRX HLB |
19.0 | |
|
PEG 6000 ML |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
light amber solid | |
|
MELTING POINT |
60 - 62 C | |
|
ACID VALUE |
5 max | |
| SAP VALUE |
7 - 13 | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.080 ± 0.010 | |
| CLOUD POINT (1% H2O) |
> 100 C | |
|
APPRX HLB |
19.3 | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
|
|
||